Neuromodulators and hormones are chemical messengers critical in the body’s communication and regulation of physiological processes. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands, while neurons in the nervous system release neuromodulators.
Today’s article will discuss the differences between hormones and neuromodulators. Read until the end and discover if these treatments can work for you.
What are Neuromodulators?
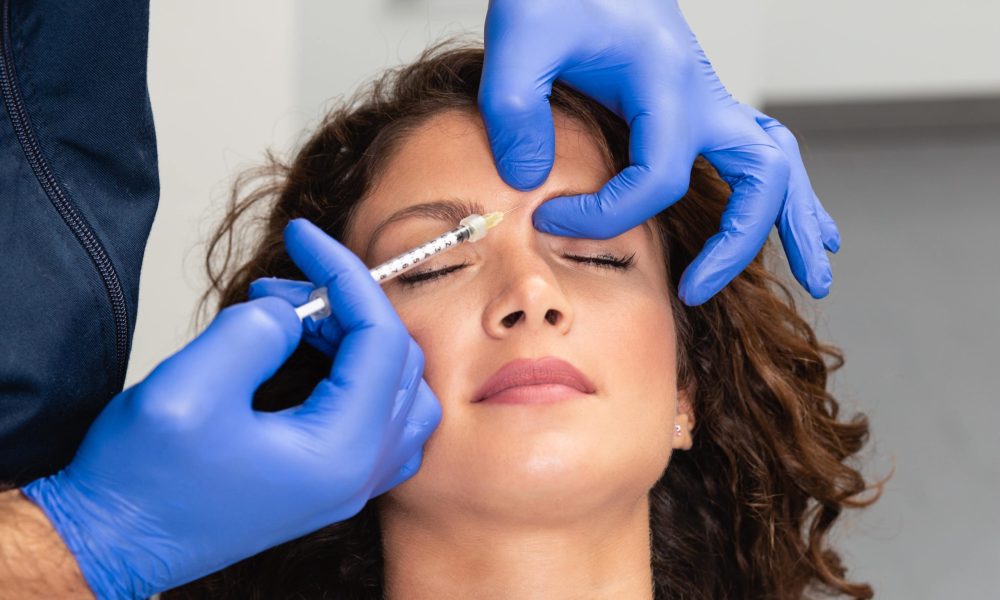
Neuromodulators are a type of chemical messenger that is released by neurons in the nervous system. Regarding cosmetic treatments, neuromodulators and hormones may play a role, but they differ in their mechanisms of action. Neuromodulators, such as botulinum toxin (Botox), block the signals that travel between nerves and muscles. This results in temporary muscle paralysis and can be used to smooth out wrinkles and fine lines on the face.
As collagen reduces, the wrinkles on your skin become more prominent, especially if you often squint or perform similar expressions. Neuromodulators are wrinkle muscle relaxers. They consist of ingredients to paralyze the muscles within the area. This feature reduces moderate to severe facial wrinkles. The solution we use has several strengths for maximum customization. Experts administer neuromodulators with an injection into the muscle. Neuromodulators are FDA-approved to treat lines between the brows (called the “11’s”), severe frown lines, and other skin conditions.
The advantages of neuromodulators include the following:
- Diminish lines
- Reduce wrinkles
- Remove frown and forehead lines
- Soften crow’s feet, forehead, and brows
- Minimize bunny lines on the nose
- Erases lines near the mouth and eyes
- Rejuvenates your neck
- Reduces excessive sweating
- Non-surgical treatment
- No recovery
Botox and Dysport
Botox and Dysport are two popular neuromodulators commonly used in cosmetic treatments. These injectables work by blocking nerve signals to specific muscles, which helps to reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
Botox and Dysport contain a purified form of botulinum toxin type A, a neurotoxin produced by Clostridium botulinum. When injected into the muscle, the toxin prevents the release of a chemical called acetylcholine, which is responsible for muscle contractions. This step leads to temporary muscle relaxation, which can help smooth out wrinkles and fine lines.
While Botox and Dysport are similar neuromodulators in many ways, there are some critical differences between the two. Dysport tends to diffuse more quickly than Botox, making it a better option for treating larger areas, such as the forehead. On the other hand, Botox may be a better choice for more precise treatments, such as around the eyes.
Botox and Dysport are considered safe and effective when administered by a qualified healthcare professional. However, as with any medical treatment, there are potential risks and side effects. These rare cases can include temporary redness, swelling, and bruising at the injection site and more severe complications.
If you are considering Botox or Dysport as a neuromodulator treatment, you must consult a qualified healthcare provider to determine whether these options suit you. They can help you understand the risks and benefits of each treatment and work with you to develop a personalized plan to achieve your desired results.
What are Hormones?
Hormones, conversely, are chemical messengers secreted by endocrine glands into the bloodstream, where they travel to distant target cells or tissues. Regarding cosmetic treatments, neuromodulators and hormones may play a role, but they differ in their mechanisms of action. On the other hand, hormones are chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to regulate various bodily functions. Hormone therapies for cosmetic purposes, such as estrogen replacement therapy, can help improve the appearance of the skin by increasing its thickness and elasticity.
Difference Between Hormones and Neuromodulators
Cosmetic treatments have significantly evolved over the years. Various cosmetic treatments are available that help improve one’s physical appearance. Two of the most popular cosmetic treatments are neuromodulators and hormones. Although they seem similar, they are different in their function and effects.
Neuromodulators are substances that affect the function of neurons. They work by blocking the release of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, which is responsible for causing muscle contractions. By blocking acetylcholine, neuromodulators prevent the muscles from contracting, reducing wrinkles and fine lines. The most commonly used neuromodulator in cosmetic treatments is botulinum toxin, also known as Botox.
On the other hand, hormones are chemical messengers that are produced by various glands in the body. They regulate different bodily functions, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Hormones used in cosmetic treatments are usually synthetic versions of naturally occurring hormones. The most commonly used hormone in cosmetic treatments is estrogen.
One of the critical differences between neuromodulators and hormones is their mechanism of action. Neuromodulators work locally, specifically on the muscles that cause wrinkles and fine lines. On the other hand, hormones work systemically, affecting various bodily functions.
Another difference between the two is their duration of action. Neuromodulators typically last for three to six months, after which the effects gradually wear off. Hormones, however, can last for several months to years, depending on the type of treatment.
Regarding safety, both neuromodulators and hormones are generally safe when administered by a qualified healthcare professional. However, neuromodulators are more commonly associated with side effects such as bruising, swelling, and muscle weakness. On the other hand, hormones can cause more systemic side effects such as headaches, mood changes, and weight gain.
Why Neuromodulators are Better than Hormones
Neuromodulators and hormones are important signaling molecules in the body, but there are some critical differences between the two. Neuromodulators are generally better than hormones because they act more quickly and precisely.
Unlike hormones, which are typically released into the bloodstream and can take some time to reach their target cells, neuromodulators are released directly into the synapses between nerve cells. This factor allows them to act more quickly and precisely, as they can target specific cells or groups of cells with greater accuracy.
Additionally, neuromodulators can be more flexible in their actions than hormones. Hormones typically have concrete steps and are produced in response to particular stimuli, whereas neuromodulators can be released in a more dynamic and context-dependent way. This aspect allows the nervous system to respond more quickly and adaptively to changing conditions.
Overall, while both neuromodulators and hormones play essential roles in the body, neuromodulators offer some distinct advantages in terms of speed, precision, and flexibility of action.
Final Takeaways
In conclusion, neuromodulators have proven to be more efficient than hormones in several aspects. Unlike hormones, which are synthesized in glands and travel through the bloodstream to reach their target, neuromodulators are released locally in the nervous system, allowing for faster and more precise signaling. Additionally, neuromodulators have a more specific and targeted effect, allowing them to impact neural communication and behavior significantly. Overall, neuromodulators have shown to be a valuable tool in studying the nervous system and have opened up new possibilities for treating neurological disorders.
If you want to experience neuromodulators, our amazing friends at R & R Aesthetic Medicine can help you today. Visit them now!